title:
style: nestedList # TOC style (nestedList|nestedOrderedList|inlineFirstLevel)
minLevel: 0 # Include headings from the specified level
maxLevel: 0 # Include headings up to the specified level
includeLinks: true # Make headings clickable
debugInConsole: false # Print debug info in Obsidian consoleBasic Knowledge of Metal Computing
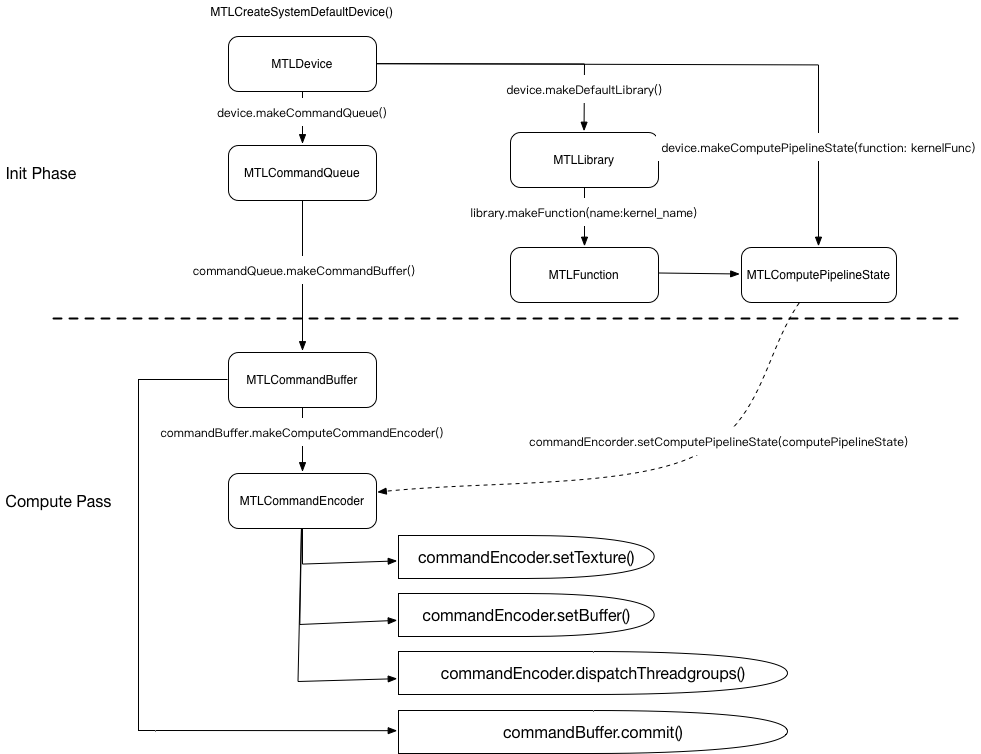
Metal 除了可以做 GPU 加速图形渲染任务之外,还能使用 GPU 来进行大规模的计算,我们称之为 GPGPU(Generic-Purpose GPU),这样能加速很多复杂的计算,比如当前最热的深度学习等。
每次运算可以看做是一次 GPU 指令的 Buffer(MTLCommandBuffer),通过通过计算的 Encoder(MTLComputeCommandEncoder)将计算资源(MTLResource)上传到 kernel 计算函数(MTLFunction)中,最后分配(dispatch)到多个线程去执行,来完成通用计算。
Grid, ThreadGroup, Thread
Metal 将一次大规模的运算理解成 1 个大的网格,然后将网格又划分成 n 个线程组,每个线程组又包含有 m 个线程。
n 和 m 都是可以至高使用 3D 的 MTLSize 表示,如果是 2D 的计算模式,可以将 depth 设置为 1,如果是 1D,需要将 height 和 depth 同时设置为 1。
typedef struct {
NSUInteger width, height, depth;
} MTLSize;Calculate Thread and ThreadGroup in Shader
有了上述的概念之后,我们就可以在我们的 kernel 函数中去获取 当次计算对应的位置 了。
Metal 的 kernel 函数,每次计算相当于 一个 thread,我们可以通过 Metal 的内置标识去获取到当前计算与网格的位置。
比如在本 demo 中需要取的是当次计算相对于网格的位置,可以使用 [[ thread_position_in_grid ]] 标识:
kernel
void ComputeKernelShader(device uint *outBuffer [[ buffer(0) ]],
constant uint2 &outSize [[ buffer(1) ]],
uint2 position [[ thread_position_in_grid ]]) {
if (position.x > outSize.x || position.y > outSize.y) {
return;
}
uint idx = position.y * outSize.x + position.x;
outBuffer[idx] = idx;
}常用的内建标识有:
-
uint2 [[ thread_position_in_grid ]]当次计算的 线程 在计算 网格 的位置
具体在红点的位置,该值就是
uint2(9, 10) -
uint2 [[ threadgroup_position_in_grid ]]当次计算所属的 线程组 在 网格 的位置
具体在红点的位置,该值就是
uint2(1, 2) -
uint2 [[ thread_position_in_threadgroup ]]当次计算的 线程 在 线程组 的位置和上图一样,恰好也是
uint2(1, 2) -
uint2 [[ threads_per_threadgroup ]]每个线程组线程的 数量上面两个图的都是返回
uint2(8, 4)
他们 4 者是有转化关系的:
thread_position_in_grid = threadgroup_position_in_grid * threads_per_threadgroup + thread_position_in_threadgroup即
(9, 10) = (1 * 8 + 1, 2 * 4 + 2)
2D Compute Grid Distribution
一般来说,比如对图片处理的网格分布,网格都是 2D 的。
根据设备的不同,MTLComputePipelineState 会有最佳的执行线程数量和线程组最大的可执行线程数量:
-
threadExecutionWidth最有效率的线程执行宽度,最好是该返回值的倍数 -
maxTotalThreadsPerThreadgroup每个线程组最多可以有多少个线程
这样就可以得出我们线程的 线程组分布 :
NSUInteger w = _computePipelineState.threadExecutionWidth; // 最有效率的线程执行宽度
NSUInteger h = _computePipelineState.maxTotalThreadsPerThreadgroup / w; // 每个线程组最多的线程数量
_threadsPerThreadGroup = MTLSizeMake(w,
h,
1);然后可以根据上面的 w & h 以及要计算的总宽高 totalWidth & totalHeight 计算出线程组在 计算网格的分布:
_threadgroupsPerGrid = MTLSizeMake((totalWidth + w - 1) / w,
(totalHeight + h - 1) / h,
1);此处计算的结果是 大于等于 实际用到的线程组分布的但是最终的分布依然会是一个矩形,多余的部分会在最后(最右或者最底)进行 padding。
比如说,一个 11x7 的图片,每个线程组分布的 size 为 4x4x1,那么根据上面的计算,计算得线程组在网格分布如下:
totalWidth = 11
totalHeight = 7
w = h = 4
_threadgroupsPerGrid.w = (totalWidth + w - 1) / w = (14 / 4) = 3
_threadgroupsPerGrid.h = (totalHeight + h - 1) / h = (11 / 4) = 2得到线程组在网格的分布为 3x2,总网格的大小是 4x4 * 3*2 = 12x8,相比 11x7 在最右和最后作 padding:

红框的就是 padding 的线程,是无用的,因此在 shader 计算的时候需要剔除它们。
kernel
void ComputeKernelShader(device uint *outBuffer [[ buffer(0) ]],
constant uint2 &outSize [[ buffer(1) ]],
uint2 position [[ thread_position_in_grid ]]) {
if (position.x >= outSize.x || position.y >= outSize.y) {
return;
}
// .......
}当超越了边界的时候,直接 return,说明本次 shader 调用是无用的,不参与到计算中。
Demo
本 demo 的目的是将 1024x1024 的二维数组从左到右从上到下 +1 递增排列,如下图所示。

demo 比较简单,旨在理解 Metal 通用计算的流程。
最终验证打印的结果如下:

使用 Metal 进行通用计算共有如下步骤:
1、配置 Metal setupMetal
这一步配置 Metal 的 Device 以及申请一个指令队列
- (void)setupMetal {
_device = MTLCreateSystemDefaultDevice();
_queue = [_device newCommandQueue];
}
2、配置计算管线 setupComputePipeline
使用在 .metal 文件声明的 kernel 函数,配置到计算管道中
- (void)setupComputePipeline {
id<MTLLibrary> library = [_device newDefaultLibrary];
id<MTLFunction> kernelFunc = [library newFunctionWithName: @"ComputeKernelShader"];
NSError *err;
_computePipelineState = [_device newComputePipelineStateWithFunction: kernelFunc error: &err];
NSAssert(_computePipelineState != nil, @"Failed to create pipeline state: %@", err);
}
3、构造输出的缓冲区 createOutputBuffer
计算的结果我们保存在一个缓冲区 MTLBuffer 中,这里先申请一个后续传入给 GPU 进行写入保存计算结果
- (void)createOutputBuffer {
_outputBuffer = [_device newBufferWithLength: _outW * _outH * sizeof(uint32_t)
options: MTLResourceStorageModeShared];
}
有如下注意:
-
kernel 中的 uint 使用的是 C 类型的
UInt32,所以申请的字节长度是_outW * _outH * sizeof(uint32_t) -
该 Buffer 需要被 CPU 和 GPU 都访问,因此其 options 使用
MTLResourceStorageModeShared
4、配置计算线程组 setupThreadGroups
根据 要计算的网格大小 ,此处是 1024x1024 配置线程组,在第二节的时候已经详述了,
- (void)setupThreadGroups: (NSUInteger)totalWidth totalHeight: (NSUInteger)totalHeight {
// Refer apple doc
// https://developer.apple.com/documentation/metal/calculating_threadgroup_and_grid_sizes?language=objc
NSUInteger w = _computePipelineState.threadExecutionWidth; // 最有效率的线程执行宽度
NSUInteger h = _computePipelineState.maxTotalThreadsPerThreadgroup / w; // 每个线程组最多的线程数量
_threadsPerThreadGroup = MTLSizeMake(w,
h,
1);
_threadgroupsPerGrid = MTLSizeMake((totalWidth + w - 1) / w,
(totalHeight + h - 1) / h,
1);
}5、执行计算 compute
最后是使用 Command Buffer 将 GPU 指令组装成 Encoder,这里是 MTLComputeCommandEncoder,最后提交给 GPU 计算。
- (void)compute {
simd_uint2 outSize = simd_make_uint2((uint32_t)_outW, (uint32_t)_outH);
id<MTLCommandBuffer> commandBuffer = [_queue commandBuffer];
id<MTLComputeCommandEncoder> encoder = [commandBuffer computeCommandEncoder];
[encoder setComputePipelineState: _computePipelineState];
[encoder setBuffer: _outputBuffer offset: 0 atIndex: 0];
[encoder setBytes: &outSize length: sizeof(simd_uint2) atIndex: 1];
[encoder dispatchThreadgroups: _threadgroupsPerGrid threadsPerThreadgroup: _threadsPerThreadGroup];
[encoder endEncoding];
[commandBuffer addCompletedHandler:^(id<MTLCommandBuffer> _Nonnull cmd) {
NSLog(@"Finish Computing.");
}];
[commandBuffer commit];
[commandBuffer waitUntilCompleted];
}具体如下
-
申请 Command Buffer
-
申请 Command Encoder
-
配置 Encoder
-
配置计算管道
_computePipelineState到 Encoder -
配置资源到 Encoder
-
配置 Buffer
-
配置 Texture (本 demo 不需要)
-
-
-
分配计算任务到线程组
-
提交 Buffer
注意:
为了等计算结束再进行读取,我们需要让线程等待
[commandBuffer addCompletedHandler:^(id<MTLCommandBuffer> _Nonnull cmd) {
NSLog(@"Finish Computing.");
}];
[commandBuffer commit];
[commandBuffer waitUntilCompleted];-
addCompletedHandler配置完成的回调 -
waitUntilCompleted等待执行完成再返回